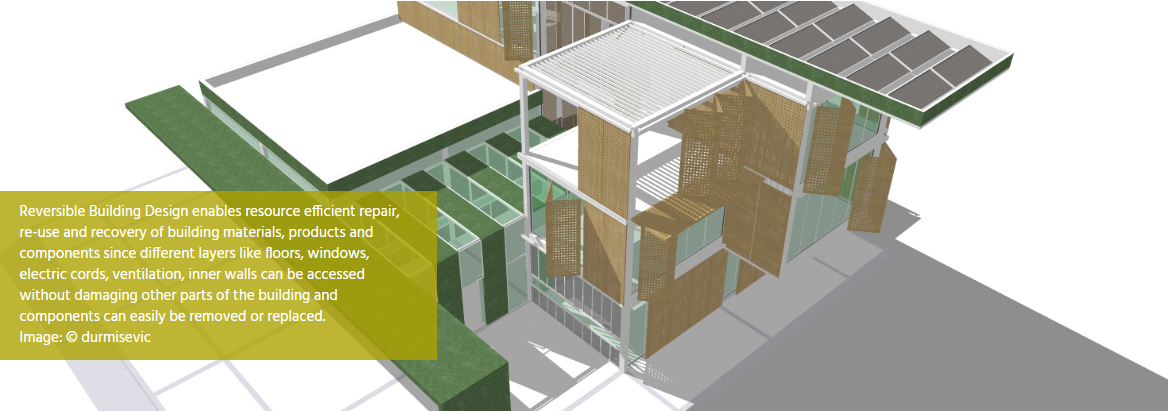
Reversible Building Design
Contents |
Definition
Reversible building is the design and construction strategy that has the ambition to realise buildings whose parts follow material loops and facilitate building alterations and support changing user needs.
Emphasising the ability of buildings and their components to return to an earlier state, this strategy strives for high resource productivity
It includes a spatial dimension, in which the building can be efficiently refurbished, as well as a technical dimension, wherein the building’s components can be disassembled and used again or deconstructed and recycled or biodegraded.
Guidelines
To bring the strategy ‘Reversible Building Design’ into practice, various principles, guidelines and techniques have already been proposed. Examples include, the generality of spaces, the adaptability and upgradability of assemblies, the durability and compatibility of building parts and the reversibility of their connections.
Moreover, as many of these design principles facilitate building transformations to changes in needs and requirements, Reversible Building is a synonym for design strategies such as Design for Change. However, whereas Reversible Building Design emphasises the establishment of material loops, Design for Change generally aspires to effective and efficient building transformations.
In BAMB, a Design Protocol for dynamic & circular building will be developed in order to enable different stakeholders in the construction value chain to implement Reversible Design strategies and approaches in construction and refurbishing activities. (For more information visit https://www.bamb2020.eu/topics/reversible-building-design/)
Related terms
Disassemble, Design for Disassembly: the act of removing components from an assembly resulting in pure material flows, facilitating their recycling or biodegradation. Design for Deconstruction is the design and construction strategy that enables the partial or total deconstruction of a building.
Deconstruct, Design for Deconstruction: the act of removing components from an assembly without damage, enabling their reuse. Design for Disassembly is the design and construction strategy that enables the partial or total disassembly of a building.
Design for Change: the design strategy based on the principle that our needs and requirements for the built environment will always change; its aim is to create buildings that support change effectively and efficiently.
Generic, Generality: a building or space that supports changing needs and requirements without physical alterations and the initiation of new material flows. Generality is the degree to which a building or space is generic.
Adaptable, Adaptability: an assembly of building materials that can be altered with a minimum of material flows initiated to support changes in needs and requirements. Adaptability is the degree to which an assembly is adaptable.
Upgradable, Upgradability: an assembly of building materials of which the condition and performance can be improved efficiently. Upgradability is the degree to which an assembly is upgradable.
Compatible, Compatibility: building parts that are designed in accordance to dimensional and possibly other standards, to ensure they are interchangeable or easy to combine.
Reversible connections: connections, i.e. physical relationship between building parts, that can be undone without damaging the parts they connect, e.g. bolts, screws, or soft lime mortars.
Circular building: a building designed according to Reversible Building principles.
Circular building products, ~ parts: building products or building parts designed according to Reversible Building principles.
References
Durmisevic E. (2006). Transformable building structures: design for disassembly as a way to introduce sustainable engineering to building design and construction (doctoral thesis). TUDelft.
Galle W. and Herthogs P. (2015). Veranderingsgericht bouwen: gemeenschappelijke taal. Mechelen: Openbare Vlaamse Afvalstoffen Maatschappij OVAM.
Oxford Advanced Learner’s Dictionary (2017). Accessed March 2017 via www.oxfordlearnersdictionaries.com. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
--BAMB - Buildings As Material Banks 09:41, 15 Aug 2018 (BST)
Featured articles and news
UK Net Zero Carbon Buildings Standard V1 published
Free-to-access technical standard to enable robust proof of a decarbonising built environment.
Prostate Cancer Awareness Month
Why talking about prostate cancer matters in construction.
The Architectural Technology podcast: Where it's AT
Catch up for free, subscribe and share with your network.
The Association of Consultant Architects recap
A reintroduction and recap of ACA President; Patrick Inglis' Autumn update.
The Home Energy Model and its wrappers
From SAP to HEM, EPC for MEES and FHS assessment wrappers.
Future Homes Standard Essentials launched
Future Homes Hub launches new campaign to help sector prepare for the implementation of new building standards.
Building Safety recap February, 2026
Our regular run-down of key building safety related events of the month.
Planning reform: draft NPPF and industry responses.
Last chance to comment on proposed changes to the NPPF.
A Regency palace of colour and sensation. Book review.
Delayed, derailed and devalued
How the UK’s planning crisis is undermining British manufacturing.
How much does it cost to build a house?
A brief run down of key considerations from a London based practice.
The need for a National construction careers campaign
Highlighted by CIOB to cut unemployment, reduce skills gap and deliver on housing and infrastructure ambitions.
AI-Driven automation; reducing time, enhancing compliance
Sustainability; not just compliance but rethinking design, material selection, and the supply chains to support them.
Climate Resilience and Adaptation In the Built Environment
New CIOB Technical Information Sheet by Colin Booth, Professor of Smart and Sustainable Infrastructure.
Turning Enquiries into Profitable Construction Projects
Founder of Develop Coaching and author of Building Your Future; Greg Wilkes shares his insights.
IHBC Signpost: Poetry from concrete
Scotland’s fascinating historic concrete and brutalist architecture with the Engine Shed.